The company is always committed to advanced manufacturing and automation, as well innovative development and application, innovative application technology is in line with the national "artificial intelligence software development/6513 Application Software Development "Strategic Emerging Industry Category Guide.In the continuous development of the year, the company has been included in the Torch Center of the Ministry of Science and Technology 2023 Qingdao No. 1 a group of high -tech enterprises identified the list of publicity; in 2023, the company's technology type 3 Small enterprises enter the warehouse number 202237021408001882. As of now, the company owns authorized 10 patents and 10 software copyrights.The company actively participates in the work of the related industry associations related to packaging and printing products, through GB/T23001 and packaging printed production process refined management and control capabilities construction. Guan's informatization and industrialization are integrated. The company continued to maintain in 2022 with the honorary title of Qingdao Specialty Special Special SMEs, the company's asset -liability ratio was 64.47%
The Internet of Things is a concentrated expression of the integration of the Internet and traditional industrial industries, and is also an infrastructure for intelligent manufacturing. Advanced IoT technology will break through data barriers in all production links and control everything wirelessly.
With the Internet of Things as the foundation, it is also necessary to create implementation nodes one by one. This requires closely focusing on key links in key manufacturing fields, in-depth research on intelligent control core devices such as simulation optimization, digital control, and intelligent measurement of manufacturing processes, and accelerating the engineering application of technical equipment such as industrial robots, human-machine intelligent interaction, and intelligent logistics management. The comprehensive presentation of the entire intelligent manufacturing system is the smart factory.
It uses information systems to control product production, achieve precise manufacturing, increase production flexibility, improve production efficiency and precision, and significantly reduce costs. Ultimately achieving true flexible manufacturing, unmanned factories, and remote collaborative production.
In this regard, "Made in China 2025" puts forward a grand vision: by 2025, key areas of the manufacturing industry will be fully intelligent, the operating costs of pilot demonstration projects will be reduced by 30%, the product production cycle will be shortened by 50%, and the defective product rate will be reduced by 50%.

lGB/T19582-2008 Industrial automation network specification based on Modbus protocol
lGB/T19760-2008CC-Link control and communication network specification
GB/T20171-2006 EPA system structure and communication specifications for industrial measurement and control systems
lGB/T25105-2014 Industrial Communication Network Fieldbus Specification Type
lGB/Z26157-2010 Fieldbus type for measurement and control of digital data communication industrial control systems
lGB/T26790.1-2011 Industrial Wireless Network WIA Specification Part 1: WIA System Structure and Communication Specification for Process Automation
lGB/T29910-2013 Industrial Communication Network Fieldbus Specification Type
lGB/T27960-2011 Ethernet POWERLINK communication profile specification
l20170053-T-339 Industrial Internet overall network architecture
l20170054-T-339 Intelligent Manufacturing Identification Analysis System Requirements
l2017-0960T-YD Industrial Internet Network Security Overall Requirements
Through the intelligent upgrading and transformation of factories, during the production process, based on real-time and accurate information, production activities can be guided, initiated, responded to, and reported to quickly respond to the production rhythm, reduce production activities without added value, and improve the efficiency of operations and processes.
Through on-site automated logistics, the transportation, storage and picking of materials can be realized automatically, accurately and quickly, achieving orderly and standardized operation of on-site logistics, improving production efficiency, and effectively reducing the labor intensity of workers.
Realize communication between upstream and downstream at the production level, provide data support for enterprises to accurately conduct various analyzes in production, and achieve refined management. Deliver plans to the workshop accurately in real time, accurately obtain feedback on workshop production, and monitor production. Linking ERP planning and production in real time makes up for the gaps in the enterprise's information architecture.
Real-time control of planning, scheduling, quality, process, equipment operation and other information allows relevant departments to discover and solve problems in a timely manner, improving the manufacturing system's ability to respond to changes.
Finally, the system is used to establish a standardized production management information platform, allowing information interconnection between the on-site control layer and management within the enterprise, and ultimately achieving lean manufacturing.
-
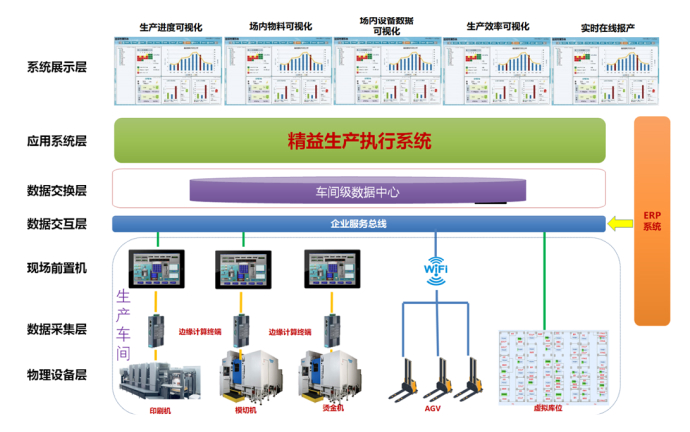
 System Topology Diagram
System Topology Diagram
This system contains five major modules: system management module, equipment management module, production process management module, data application management module and data interface management module, and warehouse management module.
System configuration is to control the running mode of applications, including configuration file management, database connection, user access control, running system management, database access management, resource access management, etc.
The system provides unified management of users who can log in to the system. User roles can be set in this module and user permissions can be set through user roles. Contains user code, user name, login name, login password, affiliation, status, user role, email, phone number, mobile phone, etc.
This system uses "role-based authority management (RBAC)" to organize the system's accessible resources and the access rights to these resources to form roles, and control the user's ability to access the system by assigning specific roles to users.
Each role is assigned different permissions and can see different pages and perform different operations. The system has preset roles such as administrator, general manager, department manager, and on-duty personnel. The administrator's permissions cannot be modified, while the permissions of the remaining roles can be modified. The top leadership role of the relevant department is set to "General Manager", and the monitoring status of all equipment under the management of each department can be viewed through the monitoring platform; the role of each department manager is set to "Department Manager", and all equipment monitoring under the management of this department can be viewed Status information; if the role of ordinary personnel on duty is set to "On Duty Personnel", they can view the monitoring status information of the equipment they are responsible for.
-
 Role management diagram
Role management diagram
Manage the processes, teams, and personnel positions of production employees, and record employee working hours, efficiency, workload and other data for performance management.
-
 Employee management diagram
Employee management diagram
Equipment management includes six sub-modules: production equipment management, AGV forklift management, sensor management, on-site front-end machine management, RFID management and on-site circulation pallet management.
Manage printing, die-cutting and hot stamping equipment, collect the operating parameters and environmental parameters of the equipment, including: machine operating speed, operating time, paper quantity, solution pH value, ambient temperature and environmental humidity and other environmental data, and match equipment according to order information Run data, match on-site worker workflow and personal production information based on personnel information, and conduct data classification, data cleaning and data calibration.
Unify the management and deployment of multiple AGV forklifts, rationally manage the operating routes of AGV forklifts based on the production plan, and display operating trajectories, operating status, battery power, fault information, task information, etc. in real time.
Manage the sensor address, location and supplier information of each device, match device information and production order information, and provide basic business data.
Manage the address, location and supplier information of the on-site front-end processor, bind the equipment process and equipment type where the front-end processor is located, and provide visual operations for employees.
-
 On-site front-end machine management example diagram
On-site front-end machine management example diagram
Manage the sensor address, location and supplier information of each device, match device information and production order information, and provide basic business data.
Through data collection and a series of intelligent hardware devices, the real-time status of the production process is tracked and real-time data of the production process is extracted.
The warehouse locations are managed in a unified manner, planned according to the actual situation of each process, and the warehouse location management logic and entry and exit rules are well established.
Clearly locate the location information and quantity information of materials in the site, conduct in-depth control through RFID, optimize the production process, extract time node information, and improve product quality.
The system opens a quality control interface during the production process, and quality inspection personnel monitor the quality data of products in the production process in real time, providing data support to ensure product quality.
The data application includes six sub-modules: digital display of production equipment, digital display of production orders, visual display of on-site materials, digital quality tracking, data intelligent statistics and product tracking and traceability.
Through display boards (TVs, LED screens, etc.), the operating data of production equipment are displayed in real time, so that production managers can clearly and quickly grasp the production status of the equipment.
Managers can grasp the order production status in real time through production order data.
Materials in the site are displayed through display boards (TVs, LED screens, etc.), and production personnel and workshop managers can grasp the status of materials in the site in real time.
Track product quality based on the quality information submitted during quality inspections during the production process, collect, analyze and utilize product quality data, and optimize the overall product structure.
Collect production tools and product information during the production process, generate statistical reports, and provide accurate data support for decision-making levels in various departments.
The products are tracked and traced based on the information collected during the production process, and accurate data support is provided for each production link.
Data interface management includes two sub-modules: ERP interface management and production equipment interface management.
The system obtains order information by regularly reading the data in the ERP database, so that the system and the ERP database information maintain consistency and integrity.
It can provide customers with a data interface to display the progress of their orders.
Based on the order information obtained from ERP, the system tracks each process of the product during the production process to ensure the integrity of the process data of the product when it is finally shipped out. If it is necessary to write back to the ERP system, it requires the cooperation of the ERP developer for customization. development.
The order information obtained in ERP includes the production process. During the order placing process, the obtained process information will be distributed to the front-end computers of all equipment.
Manage the connection between field equipment and systems, including data communication interface definitions, data communication formats, etc.
-
 System Topology Diagram
System Topology Diagram -
 System Topology Diagram
System Topology Diagram -
 System Topology Diagram
System Topology Diagram
-
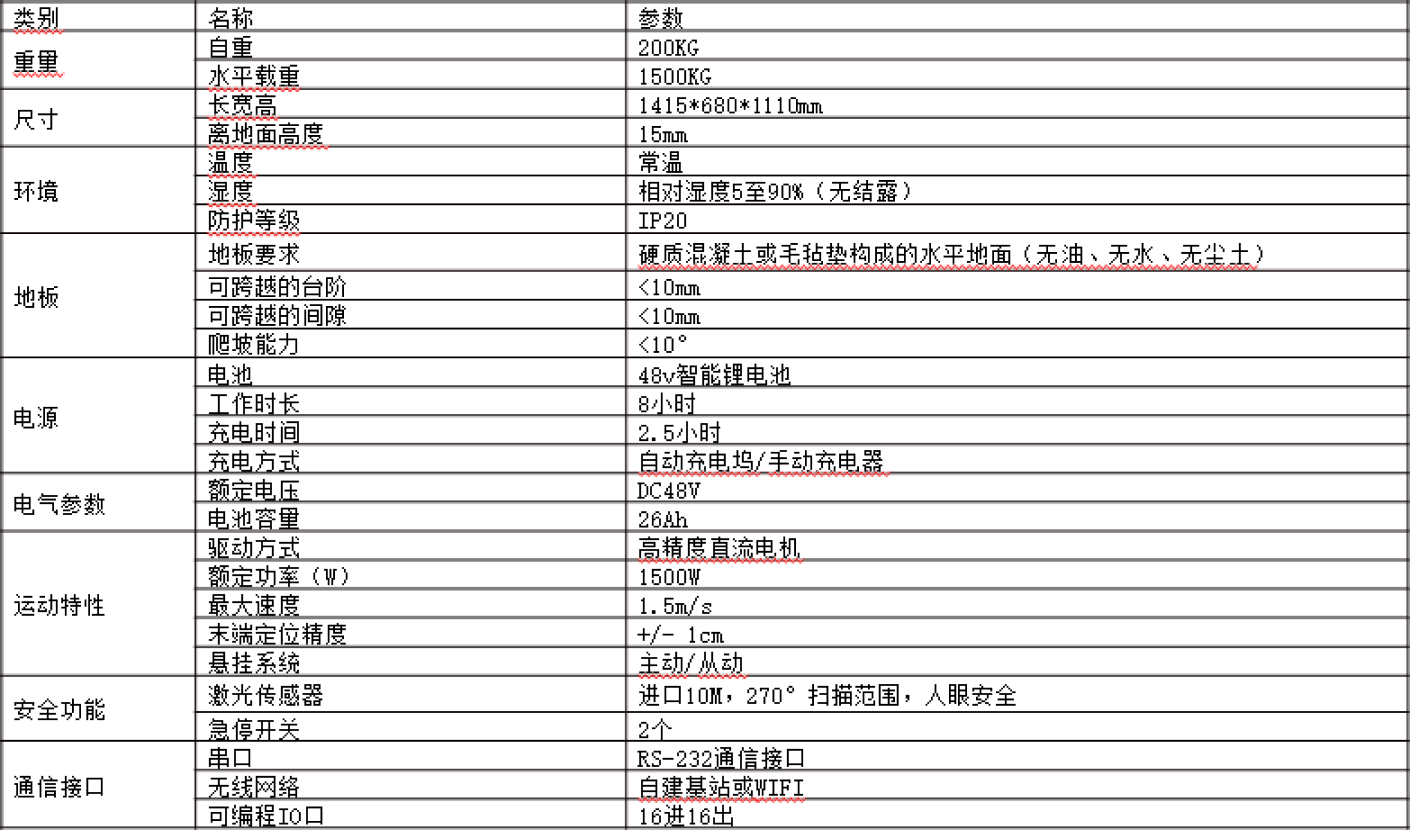
 Technical Parameters
Technical Parameters -
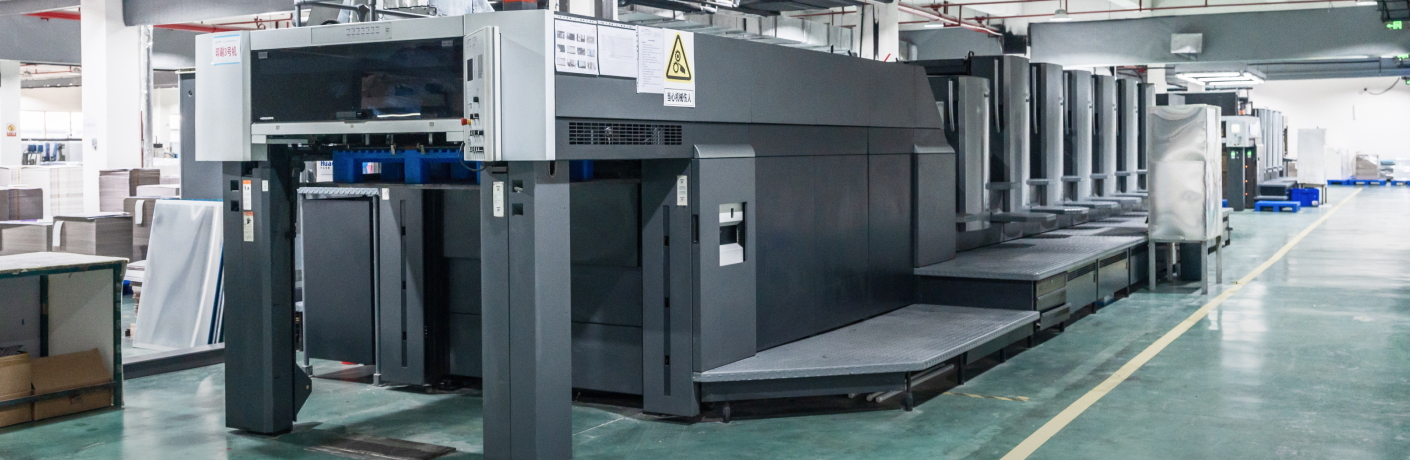
 Physical picture
Physical picture
-
 Physical picture
Physical picture -
 RFID system interface
RFID system interface
Research stage: Understand customer needs
Analysis phase: Identify goals and strategies
Define phase: establishing specific project deliverables
Design Phase: Technology and Business Process Design
Development phase: configuration, customization, system testing
Implementation phase: train and implement the solution
Optimization stage: continuous improvement after online delivery